The Problem:
Starting from rest, an aircraft accelerates to its take-off speed of 60 m s1 in a distance of 900 metres. Assuming constant acceleration, find how long the take-off run lasts. Hence calculate the acceleration.
Title: Soaring to Take-Off: Aircraft Acceleration Odyssey
Douglas Quadling Mechanics 1
Exercise 1B Q5
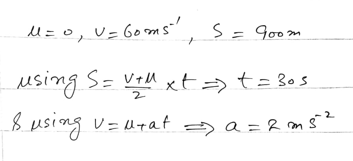
Problem Statement
Starting from rest, an aircraft accelerates to its take-off speed of 60 m/s in a distance of 900 meters. Assuming constant acceleration, find:
- How long the take-off run lasts.
- The acceleration of the aircraft.
Solution
Given:
- Initial velocity (u) = 0 m/s (starting from rest)
- Final velocity (v) = 60 m/s
- Distance (s) = 900 meters
- Acceleration (a) = constant (to be calculated)
- Time (t) = to be calculated
Step 1: Find the Time (t) for the Take-Off Run
We use the equation of motion:
s = (u + v) / 2 * t
Substitute the values:
900 = (0 + 60) / 2 * t 900 = 30 * t t = 900 / 30 t = 30 seconds
Time for the take-off run = 30 seconds
Step 2: Calculate the Acceleration (a)
We use the equation of motion:
v = u + a * t
Substitute the values:
60 = 0 + a * 30 a = 60 / 30 a = 2 m/s²
Acceleration of the aircraft = 2 m/s²
Final Answers:
- Time for the take-off run = 30 seconds
- Acceleration of the aircraft = 2 m/s²
