The Problem:

Douglas Quadling Mechanics1 Miscellaneous Exercise1 Q5
The figure shows the (t,v) graph for the motion of a cyclist; the graph consists of three straight line segments…….
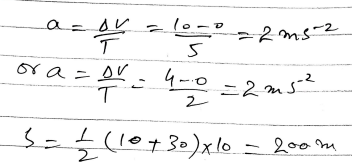
:
Total Distance Calculation
The total distance traveled by the cyclist is found by calculating the area under the velocity-time graph.
Step 1: Compute the Areas
1st segment (Triangle, 0 to 5 s):
Base = 5 s, Height = 10 m/s
Area = (1/2) × 5 × 10 = 25 m
2nd segment (Rectangle, 5 to 15 s):
Base = 10 s, Height = 10 m/s
Area = 10 × 10 = 100 m
3rd segment (Triangle, 15 to 30 s):
Base = 15 s, Height = 10 m/s
Area = (1/2) × 15 × 10 = 75 m
Step 2: Total Distance
Total Distance = 25 + 100 + 75 = 200 meters
